Project Overview
The sole purpose was to keep track of dragon sightings around the globe. When a dragon is spotted, we use the POST method to add it to our list of found dragons and add its complete description and its origin/region of sight. A text message is sent confirming it has been added. If the dragon already exists, an error is raised and a text message notifying the user of its existence is delivered. The GET request allows us to view our list of dragons as well. The project was done entirely on AWS, though there was an alternative to do it locally by using the AWS toolkit on IntelliJ IDE, installing AWS CLI, configuring AWS Serverless Application Model (SAM), an open-source framework for building serverless applications and installing Docker as a prerequisite
Workflow
The Dragons application implements a serverless architecture using AWS services. The workflow begins when a user submits a dragon sighting through the web interface. This triggers an API Gateway endpoint, which invokes a Lambda function to process the submission. The Lambda function validates the data and checks for duplicates in DynamoDB. If the dragon is new, it's added to the database, and a Step Function workflow is initiated to process the sighting. This workflow includes sending an SMS notification via SNS, storing images in S3, and updating the dragon catalog. The entire process is monitored using AWS X-Ray for distributed tracing, allowing us to identify bottlenecks and optimize performance. Authentication is handled by Amazon Cognito, ensuring that only authorized users can submit and view dragon sightings.
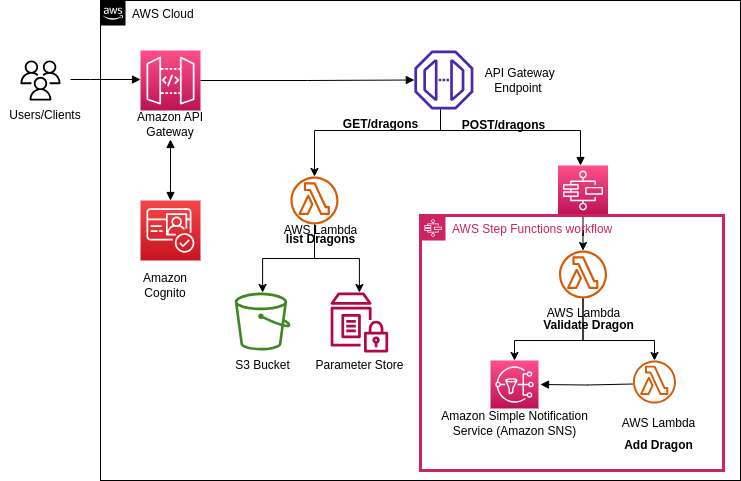
API Gateway GET Method Execution
This diagram shows the complete flow of a GET request through API Gateway to retrieve dragon sightings. The method uses Cognito for authentication and implements a Lambda proxy integration. When users request to view dragons, the API Gateway validates the request, forwards it to the Lambda function, and returns the list of dragons in JSON format with a HTTP status code 200 OK. The proxy integration allows for flexible response handling and maintains the serverless architecture's efficiency.
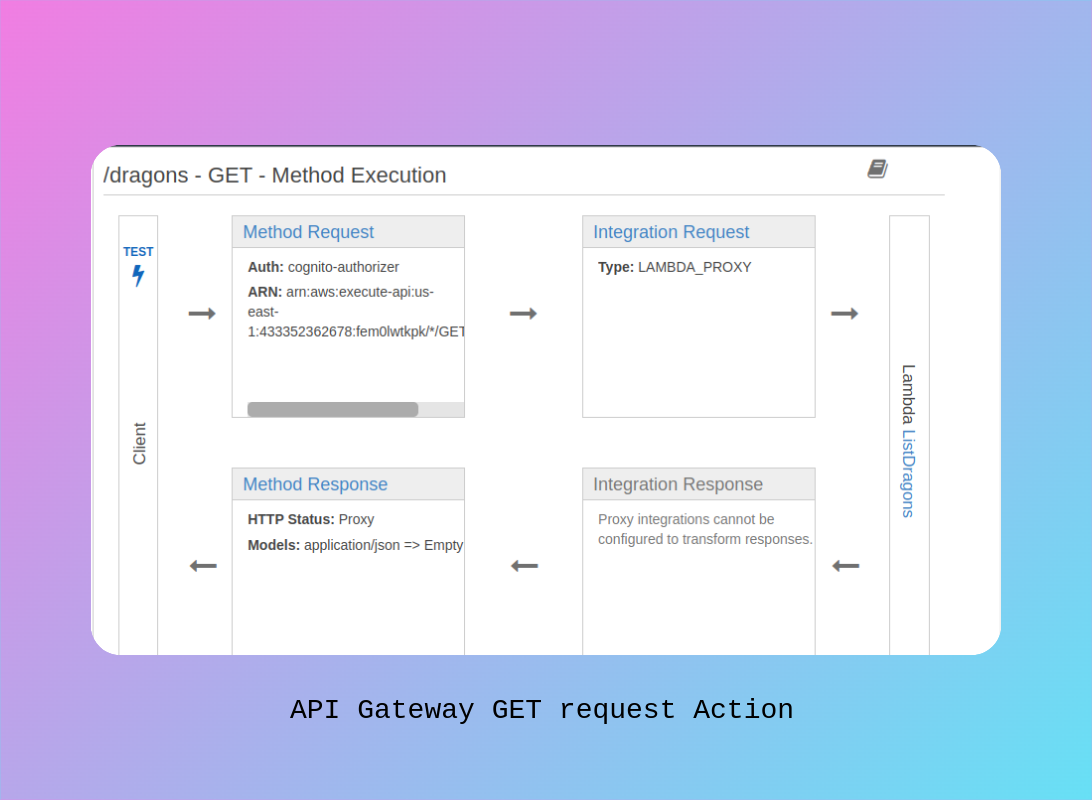
API Gateway POST Method Execution
This diagram illustrates the POST method execution flow for adding new dragon sightings. The process involves authentication through Cognito, validation of the dragon data, and integration with AWS Step Functions for complex workflow orchestration. When a new dragon is submitted, the API Gateway processes the request, triggers the Lambda function for validation, and initiates the Step Functions workflow that handles duplicate checking, data storage, and notification sending through SNS.

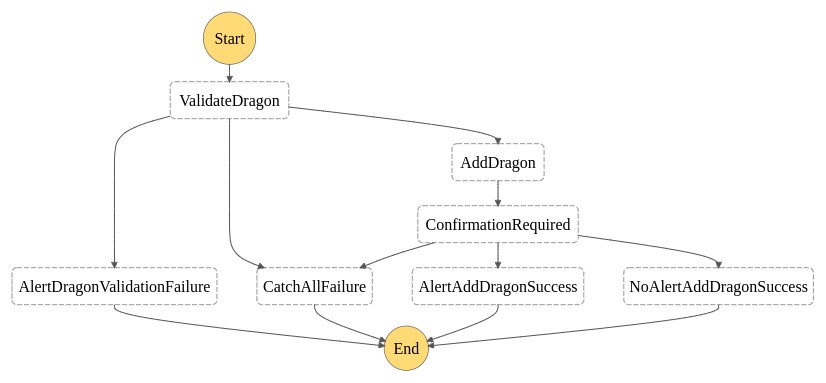
Step Functions State Machine Workflow
This state machine diagram details the Step Functions workflow that orchestrates the dragon submission process. The workflow starts with ValidateDragon to ensure data integrity, then proceeds to AddDragon for database storage. The ConfirmationRequired state acts as a decision point that branches into different notification paths. Error handling is implemented through AlertDragonValidationFailure and CatchAllFailure states, ensuring robust error management. Success scenarios are handled by either AlertAddDragonSuccess (with SMS notification) or NoAlertAddDragonSuccess (silent success), providing flexible notification options based on user preferences or system configuration.
Dragons Perks
Features
- AWS SDK for Java
- Gradle for managing dependencies and build
- Cloud9 IDE already configured with AWS CLI
Technologies Used
- Amazon API Gateway for serverless REST API hosting
- AWS Lambda for serverless compute
- Amazon Cognito for serverless authentication
- AWS Step Functions for serverless orchestrating workflows for Lambda functions
- AWS X-Ray for distributed tracing of workflows across the POST method
Resources
The AWS Well Architected Framework
whitepaper
Invoking Lambda Functions
whitepaper
Orchestration: Step Functions State Types
whitepaper
Orchestration: Step Functions Service Integration Patterns
whitepaper
Monitoring & Tracing: CloudWatch Logs in Lambda
whitepaper
Monitoring & Tracing: CloudWatch Logs in Step Functions
whitepaper
Project Details
Status
CompleteHelp Me Improve
Have suggestions, feedback, or a different perspective? I value your input! It helps me shape better work and improve as a developer.
Contact Me